Practical steps, sector-specific tactics, compliance checklists, and tools.
In Part 1 of The GST Revamp — CFO’s Strategic Playbook, we explored how India’s evolving GST regime demands a boardroom-level response from finance leaders, from proactive tax planning to governance frameworks that safeguard enterprise value.
Now, it’s time to move from strategy to execution.
This section is your hands-on GST transformation guide — packed with tools, sector-specific playbooks, compliance checklists, and real-world tactics to turn policy shifts into business advantage.
Let’s get tactical — and equip your finance team to lead GST transformation with precision and confidence.
1️⃣ CFO as Digital Enabler: Driving GST Transformation with Technology
The next wave of GST transformation is not just about new rules,
it’s about data-first decision-making, automation, and ERP alignment. As tax authorities shift toward AI-based scrutiny, CFOs must move from manual reconciliation to intelligent compliance systems that can detect anomalies, recommend corrective actions, and enhance visibility.
Automation & Reconciliation Tools
A strategic finance team can no longer rely on Excel-based processes for monthly reconciliation. Modern CFOs are deploying:
- AI-based GSTR 2A/2B vs 3B reconciliation engines
- Vendor compliance trackers
- Auto-alert systems for DRC-01C and 88C notices
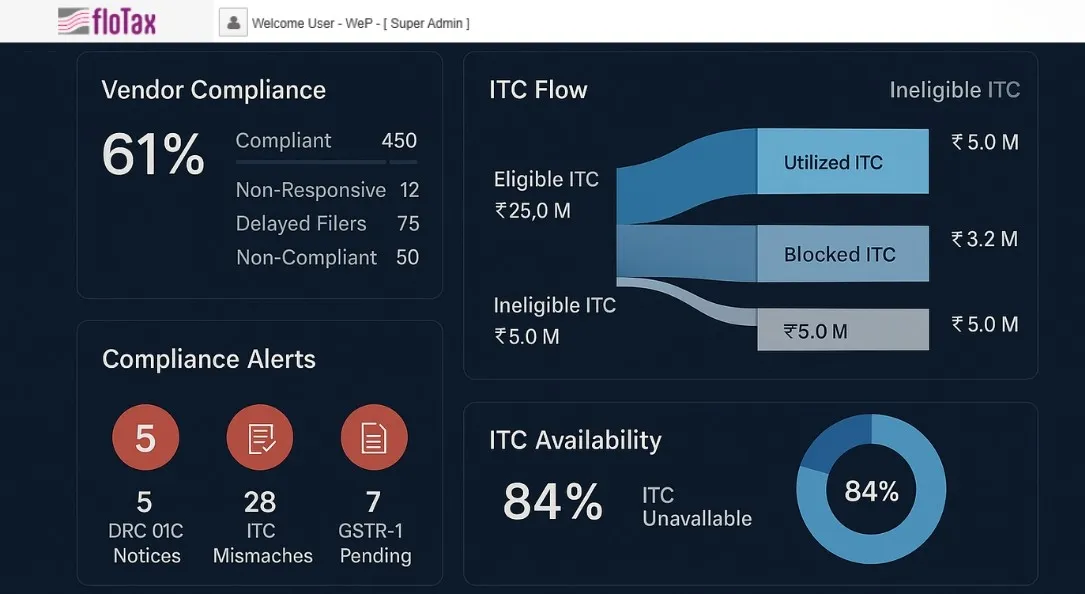
ERP Integration: From Add-Ons to Native Intelligence
CFOs are embedding GST tools directly into their SAP, Oracle, and Tally environments to:
- Automate e-invoicing and credit reconciliation
- Ensure real-time invoice validation and reporting
- Pre-validate HSN/SAC codes and place-of-supply
2️⃣ Litigation & Audit Preparedness: Playing Offense, Not Just Defense
As GST scrutiny deepens, litigation preparedness becomes a board-level priority. CFOs must move beyond reactive handling of notices to building structured, evidence-backed governance frameworks.
Audit-Readiness Checklist for CFOs
✅ Maintain vendor communication logs (WhatsApp, emails)
✅ SOPs for GSTR 2B mismatches and reversals
✅ DRC-01C/88C response workflows
✅ Legal memos outlining tax position on grey zones (e.g., canteen credits, free samples)
✅ Advance ruling tracker for key scenarios
✅ Internal GST health check every 6 months
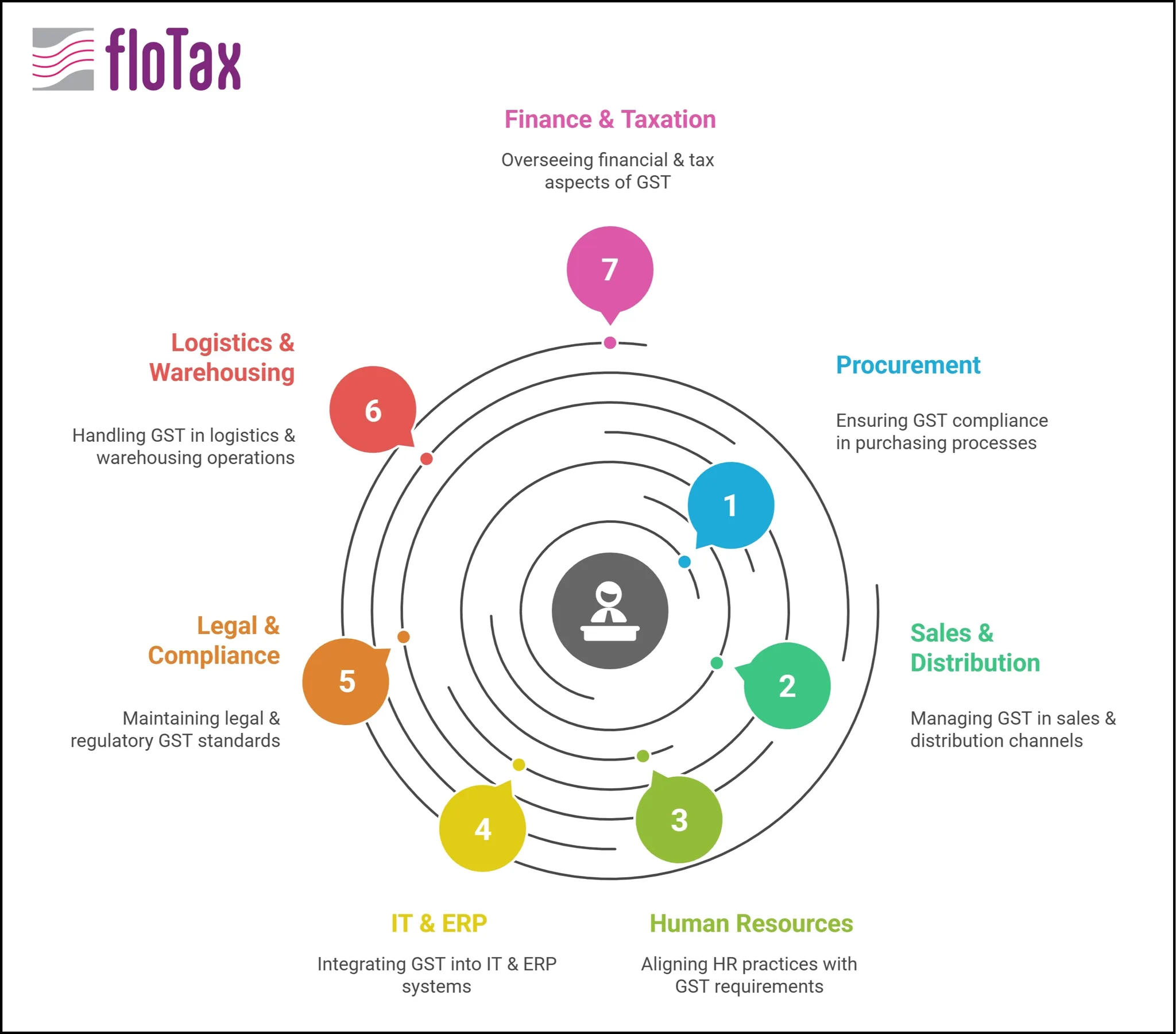
3️⃣Governance & Cross-Functional Training: Building a GST-Aware Enterprise
GST is no longer the tax team’s problem alone. It impacts:
- Sales teams (pricing, place-of-supply)
- Procurement (vendor grading, reverse charge)
- HR (employee reimbursements, canteen services)
- Logistics (e-way bills, delivery flows)
CFO’s Governance Framework
- Quarterly GST training for business teams
- Monthly compliance audits with red flags to CXOs
- Internal GST Playbook covering:
- RCM treatment
- HSN/SAC accuracy
- Common errors and mitigation
- Tax position memos
4️⃣ Strategic GST Opportunities Across Sectors: CFO View
GST compliance is not a one-size-fits-all obligation — sectoral nuances demand tailored CFO strategies. Let’s explore how strategic finance leaders in manufacturing, trading, and services are aligning GST to business growth.
4.1 Manufacturing Sector: Optimizing ITC and Workflow Efficiency
The impact of GST on manufacturing companies is two-fold:
- High volume of inward supplies → complex ITC cycles
- Capital goods and plant/machinery procurements → long-term credit planning
CFO Opportunities:
- Structure procurement contracts to align with ITC realization timelines
- Leverage advance ruling for capital-intensive projects (e.g., factory setup, tool imports)
- Automate ****e-invoicing integration with ERP to eliminate manual compliance gaps
📌CFO Tip: Monitor vendor ITC pass-through on every capex invoice — delay here can lock working capital for quarters.
4.2 Trading Sector: ITC Visibility & Pricing Intelligence
The impact of GST on traders in India is evolving due to:
- Reduced thresholds for e-invoicing
- Dependency on upstream vendor compliance
- Frequent classification disputes (goods vs. services)
CFO Opportunities:
- Establish auto-reconciliation checkpoints with key vendors
- Price products with place-of-supply rules and IGST vs CGST implications
- Train sales team to avoid non-compliant billing patterns (e.g., mismatched location billing under “bill-to, ship-to”)
4.3 Service Providers (Consulting, Trusts, NGOs, etc.)
GST on services continues to evolve, especially in:
- Charitable trusts and NGOs
- Wellness and education-based services (e.g., yoga, therapy)
- IT and software consulting with cross-border exposure
CFO Opportunities:
- Identify exempt vs taxable services (e.g., yoga therapy is exempt under certain definitions, but training courses may not be)
- Review GST rules for NGOs and Trusts to determine ITC availability
- Manage GST on services provided to charitable institutions — some may be taxable at standard rates if provided for consideration
5️⃣ Focus Areas CFOs Shouldn’t Overlook in 2025
Employee Health Insurance — Can You Claim GST Credit?
One of the most frequent CFO questions:
Can I claim GST input on employee group health insurance policies?
Answer: Only if mandated by law (e.g., Factories Act, Mines Act) — otherwise it is considered a “personal benefit” and input credit is restricted under Section 17(5).
💼 Implication: This non-creditable GST becomes a cost. CFOs must model the true effective cost of employee benefits and align procurement accordingly.
5.1 Industrial Canteens
- Canteen services provided to employees often fall in a grey zone.
- Unless the canteen is mandatory by statute, GST credit on canteen bills is typically not allowed.
✅ CFO’s Action: Structure vendor billing or employee contribution models to optimize GST treatment.
5.2 Free Goods and Promotional Offers
- As per GST law, free supply without consideration is taxable under Schedule I.
- Companies must issue invoice or delivery challan, even for promotional giveaways.
Treatment of Free Samples under GST:
- GST must be paid on supply of free goods.
- Input tax credit may need to be reversed, unless part of a composite/bundled supply.
💡CFO’s Strategy:
- Classify free items as part of combo packs (if applicable)
- Document internal memos with legal reasoning
- Align with Rule 42 and 43 ITC reversal calculations
6️⃣ Special Compliance: Slump Sale, FASTag, GSTR-9C, and More
6.1 Slump Sale and GST
A slump sale (transfer of a business unit for a lump sum) triggers GST only if it qualifies as a supply of goods or services.
✅CFOs must analyze:
- Whether “business transfer as a going concern” applies (exempt)
- Proper classification under GST Schedule II
- Agreement wording and valuation implications
6.2 E-Way Bill and FASTag Integration
- E-way bill integration with FASTag/RFID is being piloted across states.
- Mismatches between FASTag logs and e-way bill entries can trigger red flags.
6.3 GSTR-9C & Annual Filings
- Ensure audit reconciliation (GSTR-9C) is aligned with books and ERP records.
- CFOs must personally review sections prone to errors — credit reversals, stock-in-transit, etc.
✅ Checklist for CFOs:
- Cross-check turnover thresholds
- Review Section 17(5) reversals
- Map expense ledger vs credit claimed
Below are curated questions from real-time CFOs during the floTax webinar, answered by Srinivas Arya — veteran finance leader and former Group CFO, capturing actionable insights for senior finance teams.
During the Q&A session at the end of the video, the following questions were asked and answered:
❓ Q1: “How can a tax head become a CFO?”
Srinivas Arya:
To transition from a functional head to a company head, one must shift from a reactive to a proactive and strategic mindset. Key areas for development include:
- Financial Reporting: This includes IFRS, NDS, and the consolidation of accounts.
- Treasury Management: This involves managing cash flows, fundraising, working capital, and forex hedging.
- Controllership: This includes internal control, audits, and financial policies.
- Strategic Finance: This involves business planning, mergers and acquisitions, valuations, and investor relations.
❓ Q2: “What does a CFO’s calendar look like?”
Srinivas Arya:
Modern CFOs use technology to manage their calendars with updates and alarms. A typical quarterly plan might include:
- Quarter 1: Annual budget planning, GST audit planning, and ITC review.
- Quarter 2: Digital finance transformation.
- Quarter 3: Tax audits.
- Quarter 4: Year-end audit preparations.
❓ Q3: “Should taxation heads be part of every strategic decision in the CXO’s office?”
Srinivas Arya:
Yes, their participation is crucial for:
- Identifying tax-saving opportunities.
- Mitigating legal and compliance issues.
- Improving cash flow and fund flows.
- Enhancing organizational stability by addressing risk and reward.
- Structuring the supply chain for optimized procurement.
❓ Q4: “Is it necessary to be ready for litigation if we are transparent and well-documented with auditors?”
Srinivas Arya:
It depends. If documentation is transparent and explanations are clear, litigation can often be avoided. However, if there is evidence of bad intentions, it can lead to suspicion and potential litigation.
❓ Q5: “What are the ideal qualities of a CFO?”
Srinivas Arya:
A CFO should be able to integrate within and outside the organization. They need to be polite yet direct, strict with rules, and proactive in finding legal ways to conduct business.
❓ Q6: “How do you identify the correct CFO as a mentor?”
Srinivas Arya:
A mentor doesn’t have to be a CFO. It can be any senior colleague in finance who is approachable, accommodative, and patient.
❓ Q7: “How can one maintain a work-life balance in a CFO or CO role?”
Srinivas Arya:
It is important to set boundaries and maintain a disciplined routine. A fresh person working 8-10 hours can be more efficient than someone working 18 hours. While some periods may be demanding, it is crucial to prioritize family and aim for at least a 60/40 balance.
⚡Strategic Outlook: GST 2.0 and Beyond
The GST regime is shifting from compliance-checking to predictive, analytics-led governance. The next-gen features CFOs should prepare for include:
- AI-powered auto-reversals and risk predication
- Broader ITC-liquidity monitoring across multi‑state entities
- Blockchain‑based vendor authentication and crypto-linked invoices in pilot programs
- Integrated e‑way bill & FASTag data pipelines for logistics visibility
High-performing finance functions will:
- Develop GST risk dashboards and predictive tax forecasts
- Engage in scenario‑based modelling of ITC volatility
- Spearhead digital labs for pilot programs on emerging tax-tech
✅ Now you’re Ready To Transform GST Risk Into Strategic Advantage.
Transform GST Strategy into a Competitive Advantage with floTax
Ready to move beyond compliance and lead with confidence?
floTax empowers CFOs and finance teams with:
- Real-time GSTR-2B/3B reconciliation
- Automated vendor risk grading
- ERP-integrated dashboards for ITC tracking
- Smart workflows for DRC, 88C, and audit readiness
📞 Book a strategy demo with our team marcom@wepsol.com
🌐 Checkout more details on floTax here at https://wepsol.com/solutions/flotax/

